GRP
First developed in the mid-1930s, Glass Fibre Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) has become a staple in the building industry. Originally used merely for the construction of parts, the architectural advantages of GFRP were inadvertently discovered in 1967 with the attempted destruction of Disneyland’s “House of the Future”. Built between 1956 and 1957, the futuristic house was constructed entirely of fiberglass. When the attraction was deemed no longer necessary, it was scheduled to be destroyed in 1967. Amazingly, the wrecking ball merely bounced off the structure. It was at that point that the possibilities of GFRP were recognized and its use began to increase. By 1994, nearly 600 million pounds of composite materials had been used by the building industry. Today, Gulf GRC provides a variety of GFRP products to help our clients meet their building needs and realize their unique aesthetic visions.
Gulf GRC in-house design and drafting teams will work closely with you to capture your ideas on paper. Once all drawings have been approved, our sculptors will carve a model that meets your specifications.
Next, a mould will be constructed. Depending on the level of detail, it may be fabricated from fiberglass, steel, wood, or rubber. A carefully designed mix of polyester or epoxy resin and alkali-resistant glass fibres will then be sprayed into the mould. Virtually any shape or form can be moulded in this manner.
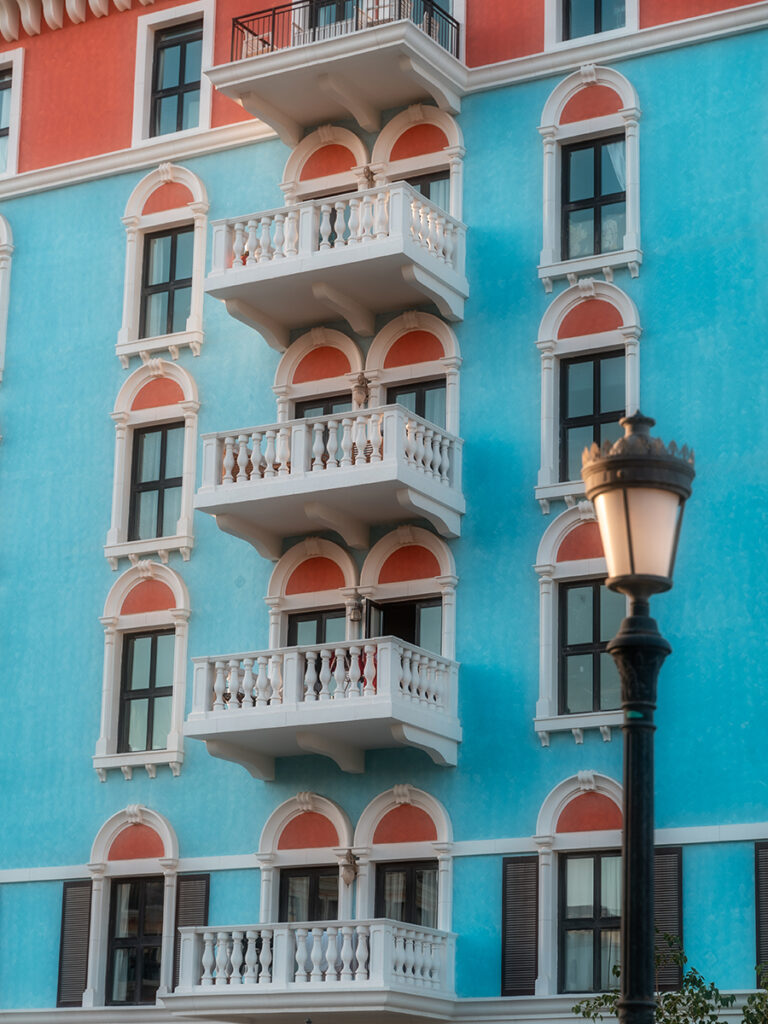
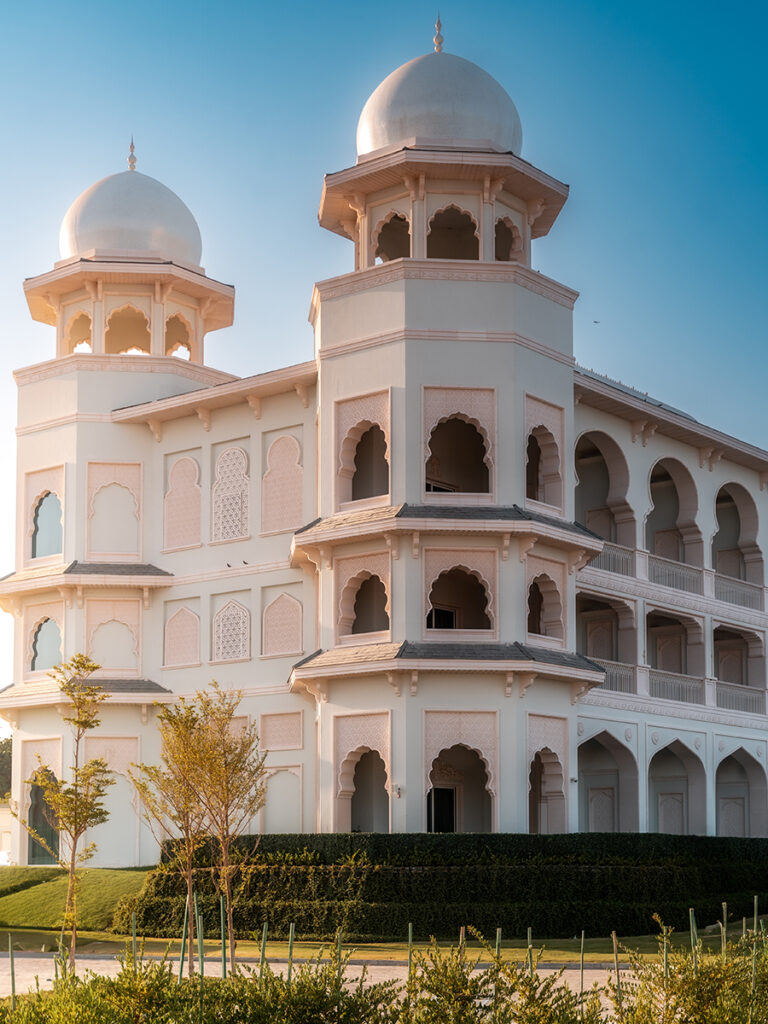
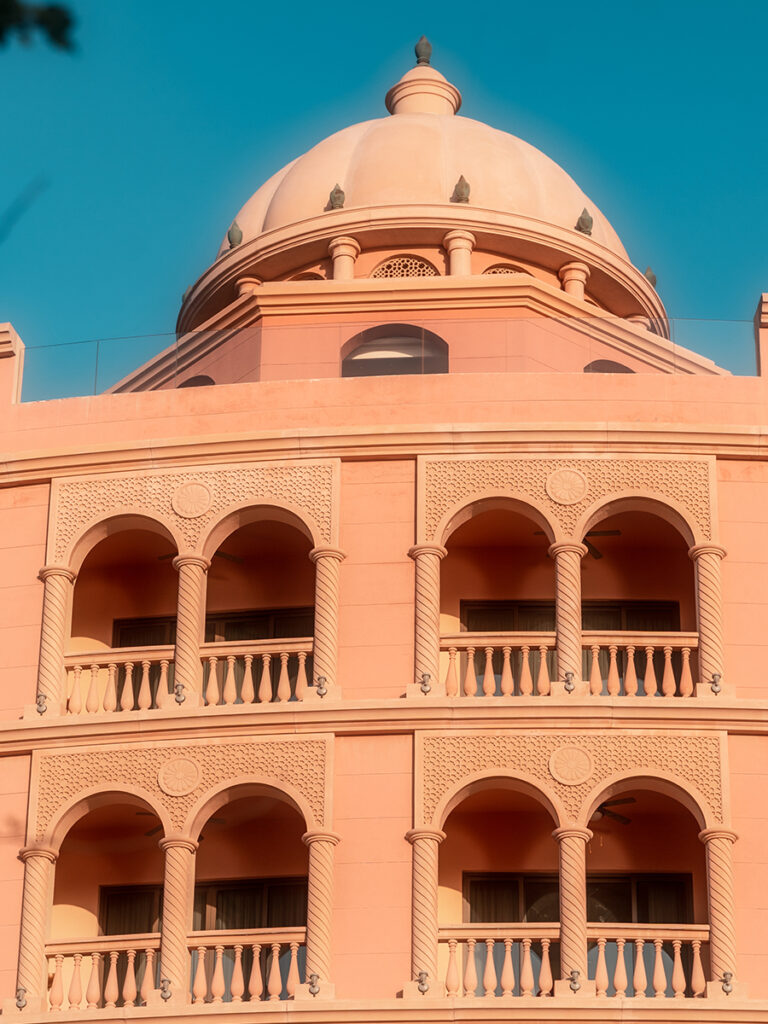
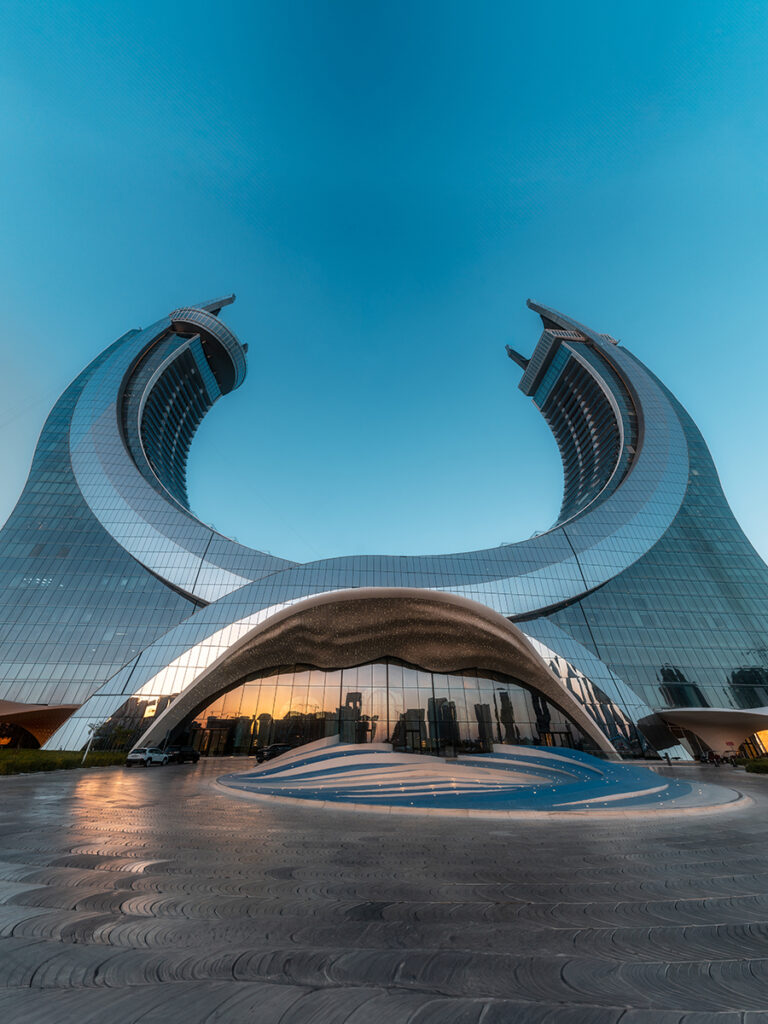
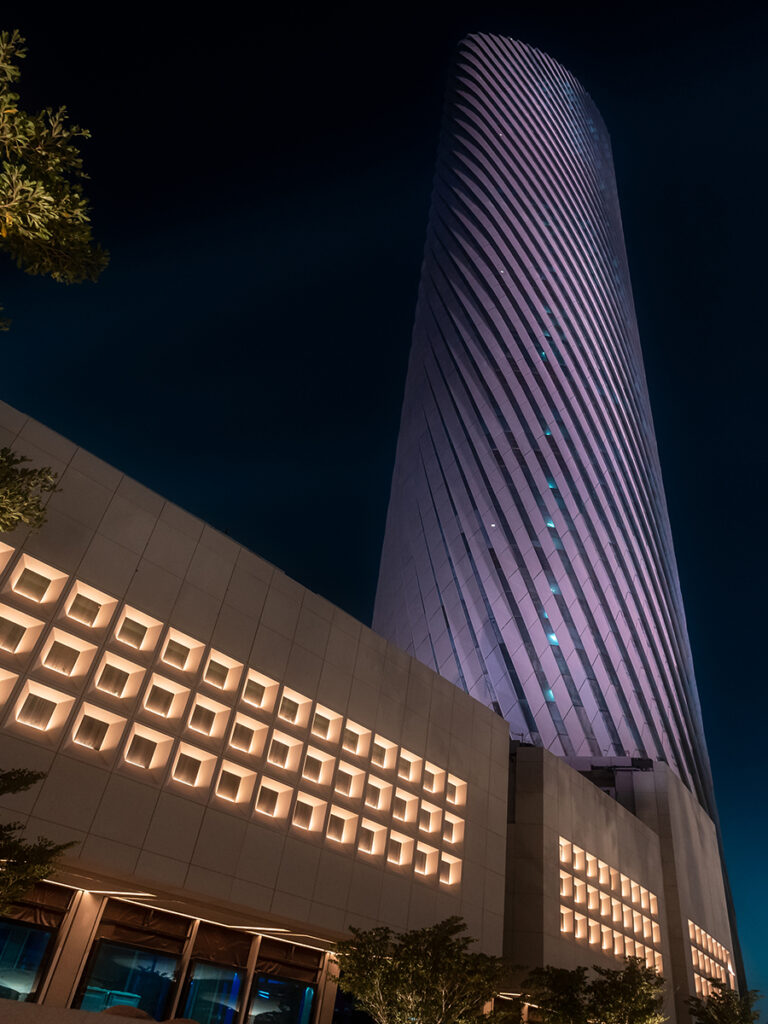
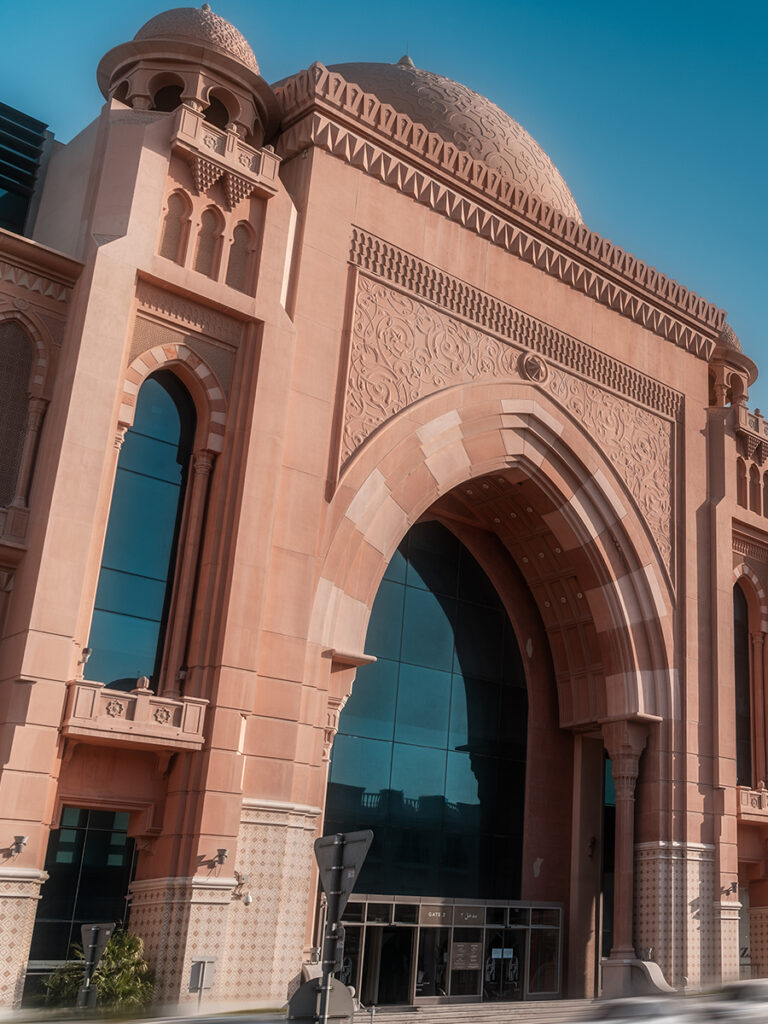
GRP (Glass Reinforced Plastic) is an extremely strong and chemically resistant product that readily lends itself to the design and construction of large structures conceived as a whole and not as an assembly of parts which have to be joined together
The introduction of this material into the construction industry has revolutionized building methods and design possibilities , as well as providing a very strong but lightweight alternative to traditional materials such as concrete, steel and timber.
Why GRP
- High Strength: GFRP has a very high strength to weight ratio. Mechanical strength that is strong and stiff for its weight that can out-perform most of the other materials (ASTM D7565, D3479, D7264,D5961, D6873)
- Lightweight: Low weights of 2 to 4 1/2 lbs. per square foot mean faster installation, less structural framing, and lower shipping costs.
- Seamless Construction: Dome and cupola sections can be adhered together to form a single watertight structure.
- Mould: GFRP Can be Moulded Into Complex Shapes: Virtually any shape or texture can be produced.
- Low Maintenance: Research shows no loss of laminate properties in GFRP after 30 years. With minimal maintenance.
- Beauty: Moulded GFRP can be meet to your needs. Bronze, wood, stone, iron, and coral can all be replicated.
- Colour Variety ( RAL code gel coats / paints and custom colours)
- Weather Proof (ASTM D570, D5229)
- Resistant Salt Water, Chemicals, and the Environment: GFRP is unaffected by acid rain, salts, and most chemicals.
- Composite: GFRP Can be manufactured with other materials (sandwich methods) to provide unique property advantages.
- Stability: GFRP products don’t corrode nor change shape.
- Anti-bacterial: Bacteria cannot survive on surface.
- Fire Resistant: Meets the requirements for Class 1 flame rating.
- Excellent Thermal Properties: Used as a thermal insulator in high heat radiation areas.
- Project Planning Advantages: Locally produced GFRP end items provide a costing advantage due to no shipping charges, more precise material control, reduced delivery time, improved lead time planning
- Project Costs Savings: Low weight to strength ratio, minimal support structure needed